Breast health remains a significant concern for many individuals worldwide. The mere mention of a breast lesion can send waves of anxiety, given the potential implications.
However, with a deeper understanding of the causes and treatments available, one can approach the situation with more clarity and less fear. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of breast lesions, their origins, and the therapeutic measures available.
Breast lesions refer to any abnormality or lump found within the breast tissue. These abnormalities can range from benign, which means they are non-cancerous, to malignant, which indicates the potential for cancer.
It’s crucial to note that not every lesion is indicative of cancer. Nevertheless, any unusual changes or discoveries in the breast should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional to ensure proper evaluation and care.
In a similar vein, understanding vaginal discharge during pregnancy can be useful, as it may change in consistency and volume due to the hormonal fluctuations occurring during this period. When discussing the causes of breast lesions, it’s helpful to categorize them based on their nature, whether benign or malignant.
Benign Causes
- Fibrocystic Changes: Predominantly found in women between the ages of 20 and 50, fibrocystic changes are the leading cause of benign breast lumps. Women may notice their breasts feeling lumpier than usual, often accompanied by pain or tenderness. Interestingly, these changes can vary in intensity throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Fibroadenomas: These are firm, non-cancerous tumors that frequently manifest in younger women. Their texture is rubbery, and they have the ability to move slightly when touched, often described as being mobile under the skin.
- Cysts: These are essentially sacs filled with fluid within the breast. On palpation, they might resemble a grape or feel akin to a balloon filled with water.
Malignant Causes
- Breast Cancer: This is, unfortunately, a well-known malignant cause of breast lesions. Breast cancer itself is a broad term, encompassing various types. The most common among these are ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive ductal carcinoma.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer: This is a less common but notably aggressive form of breast cancer. It is characterized by the breast appearing inflamed, exhibiting redness and swelling.
Risk Factors Contributing to Breast Lesions

Several factors can elevate the risk of developing breast lesions:
- Age: As women age, the risk of breast lesions, particularly malignant ones, tends to increase.
- Family History: Genetics plays a role. Having close family members who have had breast cancer can heighten one’s risk.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Extended use of hormone replacement therapy has been linked to an increased risk of breast lesions.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to high doses of radiation, especially at a younger age, can elevate the risk.
- Menstrual History: Women who started menstruating early or experienced menopause later than usual have prolonged exposure to female hormones, which can increase the risk.
Diagnosing Breast Lesions
The process of diagnosing breast lesions involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: This is the initial step where a healthcare provider will thoroughly examine both breasts, searching for any lumps or abnormalities.
- Mammography: This involves taking an X-ray of the breast and is the standard method for screening potential breast cancers.
- Ultrasound: This technique employs sound waves to generate images of the breast’s interior, providing a clearer view of any abnormalities.
- Biopsy: In cases where there’s a significant concern, a small sample of the breast tissue might be extracted and then meticulously examined under a microscope.
Exploring Treatment Options
The treatment approach largely depends on the nature of the lesion:
- Monitoring: For lesions deemed benign, healthcare professionals might suggest periodic check-ups to observe any potential changes.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention might be recommended for benign lesions causing discomfort or for malignant lesions to excise the tumor.
- Radiation Therapy: This involves using high-energy waves to target and eradicate cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment uses potent drugs to either kill cancer cells or halt their growth.
- Hormone Therapy: Particularly effective for hormone-sensitive cancers, this therapy aims to prevent the cancer from proliferating.
- Targeted Therapy: This innovative approach targets specific molecules that play a role in the growth and survival of cancer cells.
Prevention and Early Detection
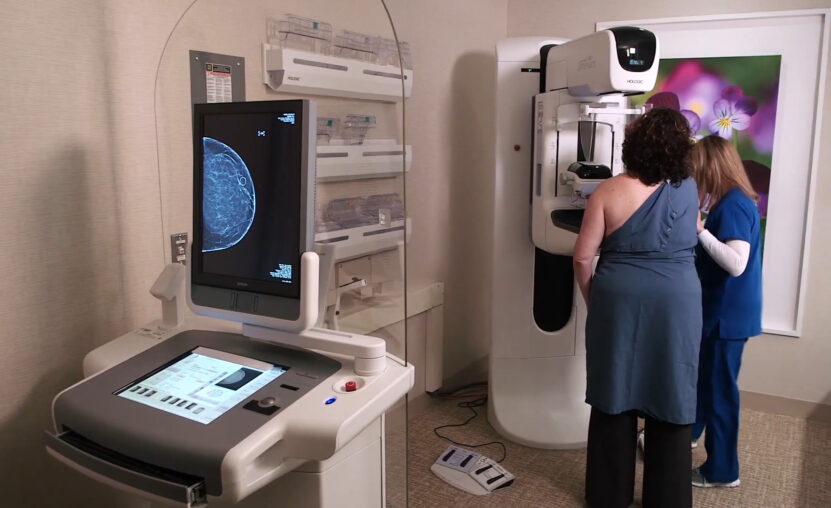
While it’s not always possible to prevent breast lesions, early detection can drastically improve prognosis. Regular self-examinations, routine mammograms, and being aware of personal risk factors are paramount.
Living with Breast Lesions
The discovery of a breast lesion marks the beginning of a journey for many. The emotional toll can be significant, given the uncertainties associated with the diagnosis.
It’s vital to seek emotional support, be it from loved ones, friends, or professional therapists. Physical changes post-treatment, such as scarring or alterations in breast shape, can also be challenging.
It’s essential to be informed about these changes and explore reconstructive options if desired. Additionally, lifestyle adjustments might be necessary, encompassing changes in diet, increased physical activity, or more frequent medical consultations.
Support Systems

Navigating the complexities of breast lesions shouldn’t be a solitary journey. Numerous support groups exist, catering to individuals diagnosed with breast lesions or breast cancer.
These groups offer a sanctuary to share experiences and coping strategies. Professional counseling can also be invaluable, helping individuals process their emotions and develop coping strategies.
Lastly, the unwavering support of family and friends can make a world of difference, offering emotional backing, assistance with daily tasks, and companionship during medical visits.
The Future of Breast Lesion Research
The realm of medical science is in a constant state of evolution. Research into breast lesions continues to make strides.
New imaging techniques are on the horizon, promising to detect breast lesions at even earlier stages. Genetic research is also shedding light on the genetic components contributing to breast lesions, paving the way for more tailored treatments.
As our understanding of breast lesions deepens, we can anticipate the development of targeted treatments with reduced side effects.
FAQs
Are all breast lesions indicative of cancer?
No, not all breast lesions are cancerous. Many lesions are benign, meaning they are non-cancerous and do not pose a threat of spreading.
However, any new or unusual breast changes should be examined by a healthcare professional to determine their nature and whether further action is needed.
How are breast lesions typically diagnosed?
The diagnosis of breast lesions often involves a combination of methods. A physical examination is usually the first step.
If a suspicious area is found, imaging tests like mammography or ultrasound may be used. In some cases, a biopsy, where a small sample of the breast tissue is taken for examination, might be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
If I have a benign breast lesion, does it increase my risk of developing breast cancer in the future?
While some benign breast conditions can slightly increase the risk of breast cancer, many do not. It’s essential to discuss your specific type of lesion and its implications with your healthcare provider to understand your individual risk better.
Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to reduce the risk of developing breast lesions?
While not all breast lesions can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of breast cancer. These include maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding hormone replacement therapy unless medically necessary.
Regular screenings and self-examinations are also crucial for early detection.
What should I do if I discover a lump or any change in my breast?
If you notice any changes in your breast, such as a lump, swelling, pain, or skin changes, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional as soon as possible. Early detection and evaluation are crucial for determining the nature of the change and deciding on the best course of action.
Concluding Thoughts
Breast lesions, while undeniably concerning, are a challenge that many confront. Armed with the right knowledge, a robust support system, and quality medical care, individuals can face this challenge head-on.
Regular screenings, heightened self-awareness, and proactive healthcare remain our best defenses against the potential threats posed by breast lesions. Prioritizing one’s health and seeking medical counsel when in doubt is always the best course of action.
